What Color Do Dogs See Humans? Unveiling the Mystery
Dogs see humans in shades of blue and yellow due to their dichromatic vision. This means they perceive colors differently than humans.
Have you ever wondered what colors dogs see when they look at us? Dogs have a dichromatic vision, which affects how they perceive the world around them. This means that dogs primarily see shades of blue and yellow, with limited ability to distinguish between reds and greens.
Understanding how dogs see colors can provide insights into their behavior and interactions with the environment. Let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of canine vision and explore how our furry friends experience the colorful spectrum of the world.
The Canine Perspective
Debunking The Color Blind Myth
Contrary to popular belief, dogs are not completely color blind. While they don’t see the world in the same way as humans, they are capable of perceiving a range of colors. The myth of total color blindness stems from the fact that dogs have fewer color receptors in their eyes compared to humans.
Science Behind Canine Vision
The science behind canine vision reveals that dogs have two types of color-detecting cells, or cones, in their eyes. These cones enable them to see a limited spectrum of colors, primarily blues and yellows. Reds and greens appear as shades of gray to them.
Contrasting Human And Dog Vision
When it comes to understanding how dogs see the world, one aspect that often piques curiosity is their color perception. Humans and dogs see colors differently due to variations in their visual systems. This article will explore the contrasting visual acuity and color perception between humans and dogs, shedding light on the fascinating world of canine vision.
Visual Acuity Differences
Visual acuity refers to the sharpness and clarity of vision. Humans have a higher visual acuity compared to dogs, allowing us to discern fine details and see objects clearly at a distance. This is primarily due to the structure and density of the photoreceptor cells in our retinas.
Dogs, on the other hand, have a lower visual acuity, meaning their ability to see fine details and distinguish between similar objects is not as refined as ours. Their retinas contain fewer cone cells, which are responsible for color vision and visual acuity. However, dogs compensate for this by having a greater number of rod cells, which are more sensitive to low light levels and motion.
Color Perception Contrast
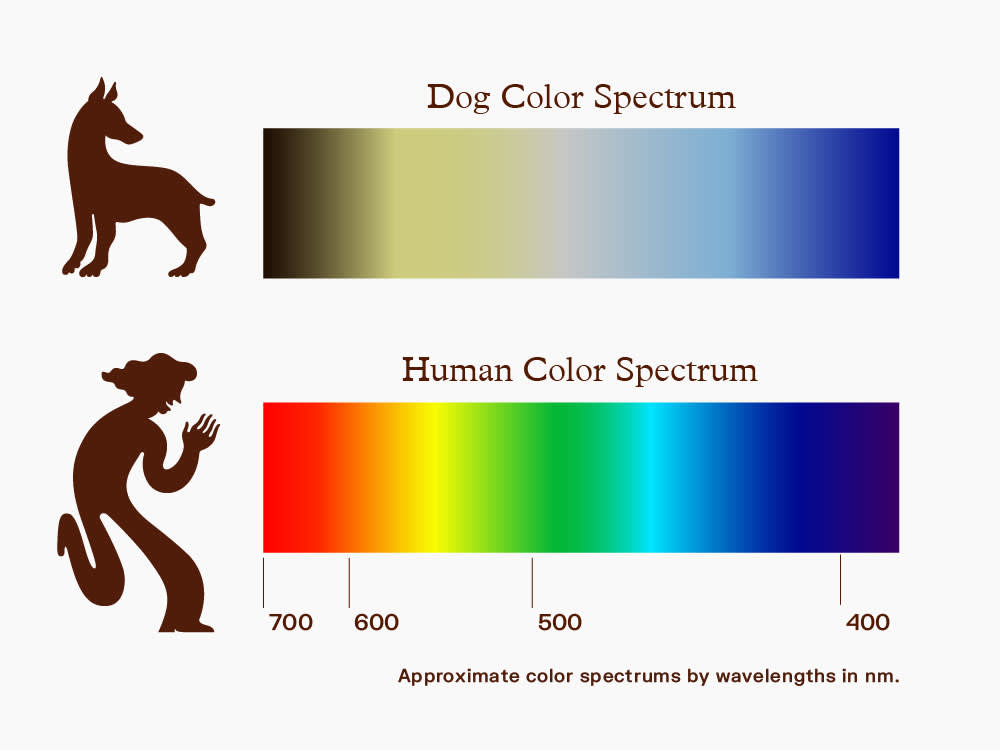
The perception of colors differs significantly between humans and dogs. While humans have trichromatic vision, with three types of cone cells that detect different wavelengths of light (red, green, and blue), dogs have dichromatic vision, with only two types of cone cells (blue and yellow). This means that dogs lack the ability to perceive the full spectrum of colors that humans can see.
To understand how dogs perceive colors, it’s helpful to imagine the world in shades of blue and yellow. Reds and greens, which appear distinct to us, may appear as shades of yellow or gray to dogs. Blue and purple hues may be more vivid to them, while certain shades of yellow and green might be challenging to differentiate.
It’s important to note that while dogs may have a limited color palette, they excel in other visual aspects, such as motion detection and low-light vision. Dogs’ vision is adapted for their natural hunting and scavenging behaviors, allowing them to track movement efficiently, even in dim lighting conditions.
In conclusion, the contrasting visual acuity and color perception of humans and dogs provide a unique perspective on how our furry companions see the world. Understanding these differences can enhance our interactions with dogs and help us create a visually stimulating environment for them.
The World Through Dog Eyes
Have you ever wondered how dogs perceive the world around them? While we humans rely heavily on our sense of sight, dogs have a different visual experience. Understanding the colors dogs see can give us valuable insights into their perception of the world. In this article, we will explore the color spectrum in dogs and how they perceive brightness and saturation.
Color Spectrum In Dogs
Dogs do not perceive colors in the same way as humans do. While humans have three types of color receptors called cones that allow us to see a wide range of colors, dogs only have two types of cones. This means that their color vision is somewhat limited compared to ours.
Research suggests that dogs primarily see the world in shades of blue and yellow. They have difficulty distinguishing between red and green colors, which appear more like shades of gray to them. So, if you’re thinking about buying a red or green toy for your furry friend, keep in mind that they might not perceive the vibrant colors as you do.
Brightness And Saturation
While dogs may have a limited color spectrum, they have a remarkable ability to detect differences in brightness and contrast. This means that while they may not see the same array of colors as humans, they can still perceive variations in light and dark.
When it comes to brightness, dogs have an advantage over humans, especially in low-light conditions. They have a larger number of rod cells in their retinas, which are responsible for detecting light. This enables them to see better in dimly lit environments, making them excellent night-time companions.
Similarly, dogs can also perceive differences in saturation, which refers to the intensity or purity of a color. While they may not see the full range of colors, they can still differentiate between shades that vary in saturation. This ability allows them to notice subtle changes in their surroundings, even if they cannot perceive the same vibrant colors as humans.
In conclusion, while dogs may not see the world in the same colorful spectrum as humans, they have their own unique visual experience. Understanding their color perception can help us create environments that cater to their needs and preferences. So, next time you choose a toy or a leash for your furry friend, consider their limited color vision and focus on other visual cues, such as brightness and contrast, to make their world a vibrant and engaging one.
How Dogs See Human Skin
Dogs see humans in shades of blue and yellow, as they have only two types of color receptors in their eyes. This means that they cannot see colors like green, red, and orange, making their perception of human skin color quite different from our own.
Dogs are known for their incredible sense of smell and hearing. However, many people are curious about how dogs perceive the world visually. One of the questions that often comes up is: what color do dogs see humans? While dogs do not see the world exactly as humans do, they are not colorblind either. In fact, dogs can see some colors, but not as many as humans. In this article, we will focus on how dogs see human skin and the factors that influence their perception.Perceived Color Tones
Dogs have fewer color receptors in their eyes than humans, which means they see fewer colors. The human eye has three types of color receptors, while the dog eye only has two. This means that dogs are dichromatic, which allows them to see shades of blue and yellow, but not red and green. Therefore, dogs perceive human skin as a shade of gray or yellowish-brown rather than the pinkish hue that humans see.Influence Of Light Conditions
The perception of human skin color by dogs can also be influenced by the lighting conditions. Dogs have a higher number of rod cells in their eyes, which are responsible for low-light vision. This means that they are better at seeing in dim light than humans. Therefore, in low light conditions, the color of human skin may appear more muted or gray to dogs. In contrast, in bright sunlight, the skin may appear more vivid to dogs, but still not as colorful as it appears to humans. In conclusion, dogs see human skin differently than humans do. While humans see skin in shades of pink, dogs perceive it as gray or yellowish-brown. This is because dogs have fewer color receptors in their eyes than humans. Additionally, the perception of human skin color by dogs can be influenced by the lighting conditions. Understanding how dogs perceive the world can help us better understand our furry friends and improve our interactions with them.Impact Of Color On Dog Behavior
Dogs see humans in shades of blue and yellow, unable to distinguish between red and green. These colors can evoke various emotions in dogs.
When training dogs, consider using blue and yellow colors for positive reinforcement, as they are more easily visible to dogs. Avoid red and green for cues or commands.

Credit: www.tiktok.com
Dog Vision In Daily Life
Dogs see humans in shades of blue and yellow due to their dichromatic vision. This affects how they perceive colors in daily life.
Navigating The Environment
Dogs rely heavily on their vision to navigate their environment. They can detect motion and see objects clearly at a distance, but their depth perception is not as accurate as humans. This means that they may have difficulty judging distances and may have trouble with tasks that require precise movements, such as catching a ball in mid-air. Additionally, dogs have a wider field of vision than humans, which allows them to see more of their surroundings at once.Interaction With Humans
Dogs see humans differently than we see each other. They are able to perceive some colors, but not as many as humans. Dogs see the world in shades of blue and yellow, with some ability to distinguish between shades of gray. This means that they may have difficulty differentiating between red and green objects. However, dogs rely more on their sense of smell and hearing when interacting with humans, which allows them to pick up on subtle cues that we may miss. In daily life, it is important to consider how dogs see the world when interacting with them. For example, using hand signals instead of verbal commands can be helpful, as dogs may have difficulty distinguishing between similar sounding words. Additionally, providing clear visual cues can help dogs better understand what we want them to do. By understanding how dogs see the world, we can improve our interactions with them and build stronger relationships.Enhancing Human-canine Communication
Using Color Cues
Dogs perceive colors differently than humans due to their limited color vision. They primarily see shades of blue and yellow, making it important to consider this when using color cues to communicate with them. Using high-contrast colors such as blue and yellow can help dogs distinguish between different objects, making it easier for them to understand visual cues from their human counterparts.
Designing For Dog Vision
When designing visual aids for dogs, it’s crucial to take into account their unique color perception. Incorporating blue and yellow hues in training tools and toys can enhance their visibility to dogs. Additionally, using these colors in dog-friendly spaces can improve their overall experience and communication with their human companions.
Credit: www.thewildest.com
Advancements In Canine Vision Research
Dogs are known for their keen sense of smell and exceptional hearing, but what about their vision? Recent advancements in canine vision research have shed light on how dogs perceive the world around them, including the colors they see and how they interpret human faces. This groundbreaking research has provided valuable insights into the visual capabilities of man’s best friend.
Recent Studies And Findings
A series of recent studies have revealed fascinating details about the color vision of dogs. Contrary to popular belief, dogs are not colorblind. While humans have three types of color receptors (cones) in their eyes, allowing them to see a wide spectrum of colors, dogs have only two types of cones. This means that dogs have dichromatic vision, which enables them to see a more limited range of colors compared to humans.
- Humans have three types of color receptors, while dogs have only two.
- Dogs have dichromatic vision, limiting their perception of colors.
- Research has debunked the myth that dogs are entirely colorblind.
Potential For Future Discoveries
With ongoing advancements in technology and scientific methodologies, there is immense potential for further discoveries in the field of canine vision. Researchers are exploring the possibility of enhancing dogs’ visual abilities through genetic and technological interventions. These developments could have far-reaching implications, not only for our understanding of canine vision but also for practical applications in various fields, such as working with service dogs and improving animal welfare.

Credit: spca.bc.ca
Frequently Asked Questions
What Color Does A Dog See A Person?
Dogs see colors differently than humans do. They have fewer color receptors, so their vision is limited to yellows, blues, and grays. Therefore, dogs see people in shades of these colors.
How Do Dogs See Humans?
Dogs see humans differently. They rely more on smell and movement than on colors. Humans appear blurry to them, but they can recognize familiar faces. Dogs also have better night vision than humans. Overall, dogs see the world in a unique way based on their senses.
What Is The Best Color For Dogs To See?
Dogs see best in shades of blue and yellow. These colors appear more vibrant to them compared to red and green. It’s important to consider their color vision when choosing toys or accessories for your furry friend.
How Do Dogs See Pink?
Dogs see pink as a shade of grey due to their dichromatic vision. They lack red-green color receptors, making them unable to see pink as a distinct color.
Conclusion
Understanding how dogs perceive colors can deepen our bond with them. While dogs see a limited color range, they rely more on other senses. By appreciating their unique perspective, we can enhance communication and companionship with our furry friends. Embracing their world enriches our relationship with them.
- Can I Get in a Taxi Without a Car Seat? - January 26, 2025
- Can I Get Chlamydia From a Toilet Seat? - January 26, 2025
- Can I Get an Uber With a Car Seat? - January 26, 2025






